Top 10 African kingdoms and empires
1. The Aksumite Empire
The Kingdom of Aksum or Axum was another name for this kingdom. This was one of the East African kingdoms that existed from 100 CE to 960 CE. Today, the empire spans Ethiopia and Eritrea. The Aksumites played an important role in the commercial trade routes that connected ancient India and the Romans.

Together with empires like Persia, Rome, and China, the empire was regarded as one of the four superpowers during its era. The Kingdom ruled over Northern Sudan, Yemen, Djibouti, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Southern Egypt, and Southern Saudi Arabia. A number of stelae were erected by the populace throughout the pre-Christian era to serve as monuments. The Obelisk of Axum, an important landmark in Ethiopia that dates back to 1700 years, is one famous structure. The people did provide the groundwork for the Ethiopian Orthodox Church once they became Christians, though. The empire is thought to be where the Ark of the Covenant rests today.
2. The Kingdom of Ghana
This well-known empire was dispersed over portions of what are now Senegal, Mauritania, and Mali. Between the years 700 until 1240 CE, the empire was in power. It was sometimes referred to as Wagadu and served as a significant halt on the trans-Saharan commerce route that connected African communities. Despite having an inadequate water supply, the empire was home to between 15,000 and 20,000 people.
Due to their expertise in the trade of kola nuts and gold, the empire was known as the Land of Gold. Large armies and complex tax and administrative systems are thought to have been there. Gold mining was the empire’s source of power, and camel adoption improved their gold trading.
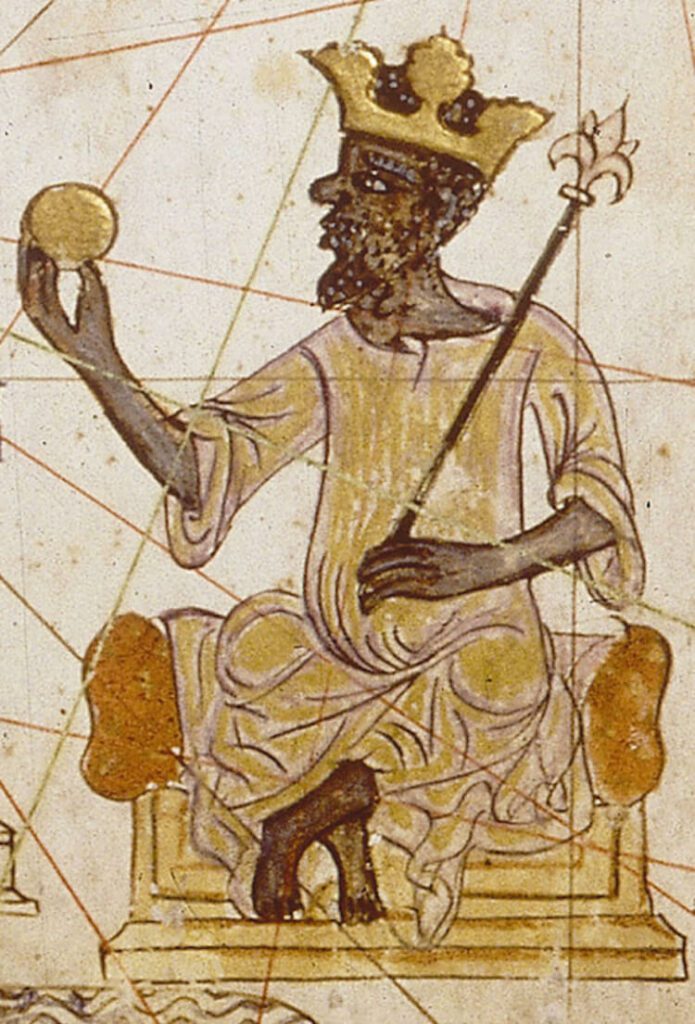
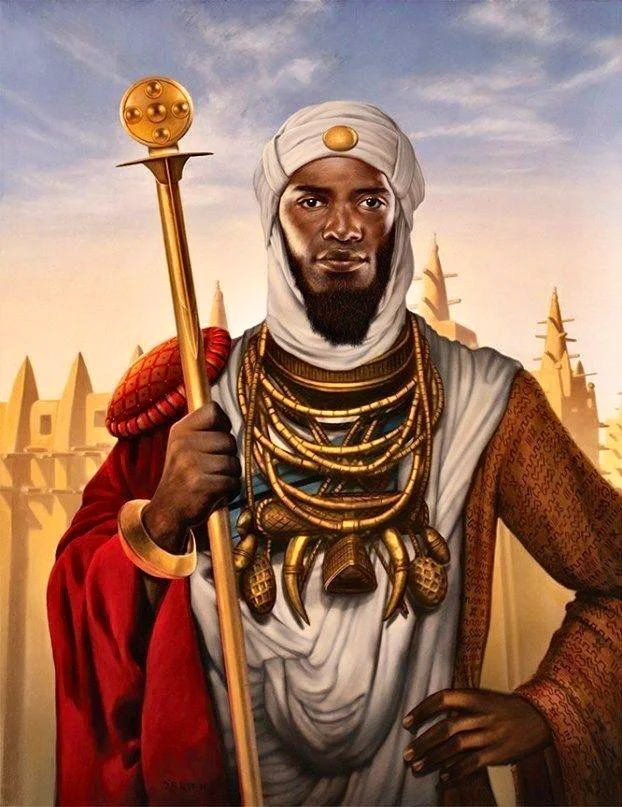
3. The Mali Empire
A portion of Guinea, Ivory Coast, The Gambia, Guinea-Bissau, Mali, Niger, Senegal, and Mauritania are now part of the Kingdom. Between the years 1230 and 1670, the empire was active. The populace extracted gold from their mines, making their ruler, Mansa Musa, the wealthiest.
4. The Songhai Empire
Today, this well-known kingdom is dispersed across portions of Mauritania, The Gambia, Senegal, Mali, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Burkina Faso, Niger, and Nigeria. Between the years 1000 and 1591, the empire was active. It was regarded as the biggest state on the African continent because it was one of the African kingdoms before colonization.
Timbuktu, one of its most notable cities, served as a hub for education in the area. Following the collapse of the Mali Empire, the empire arose, and during this time, it was responsible for the expansion of several significant trans-Saharan routes.
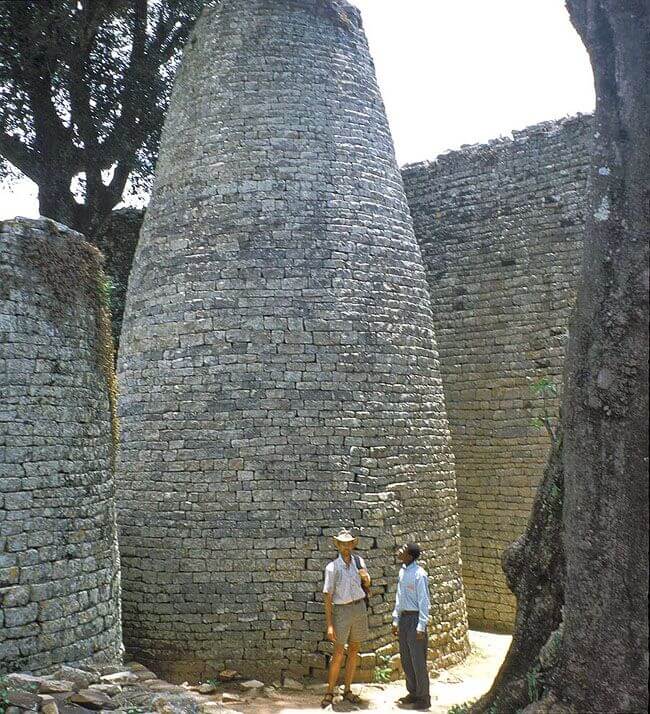
5. The Kingdom of Zimbabwe
Between 1220 and 1450 CE, this kingdom was active. Today, it is one of the African kingdoms and claims Great Zimbabwe, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, as its capital. Around 18,000 people lived in the empire, who covered an area of around 7 km2. From the continent’s southeast coast to its interior, the empire controlled the commerce in gold and ivory. They also mined copper and iron.
6. The Kingdom of Mutapa
What is currently South Africa, Lesotho, Zambia, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, and Swaziland were all part of the empire. This empire was one of the South African kingdoms that flourished between the years 1430 and 1760. It covered a sizable portion of Southern Africa, from the Indian Ocean coast up the Limpopo and Zambezi rivers.
The Kingdom of Mutapa is thought to have been founded by a military prince from the Kingdom of Zimbabwe. In an effort to dominate trade in the area, the Portuguese eventually took the role of middlemen between India and the smaller Mutapa kingdoms. The empire quickly grew to be so powerful that any Portuguese commander who assumed office had to pay a tribute to them.
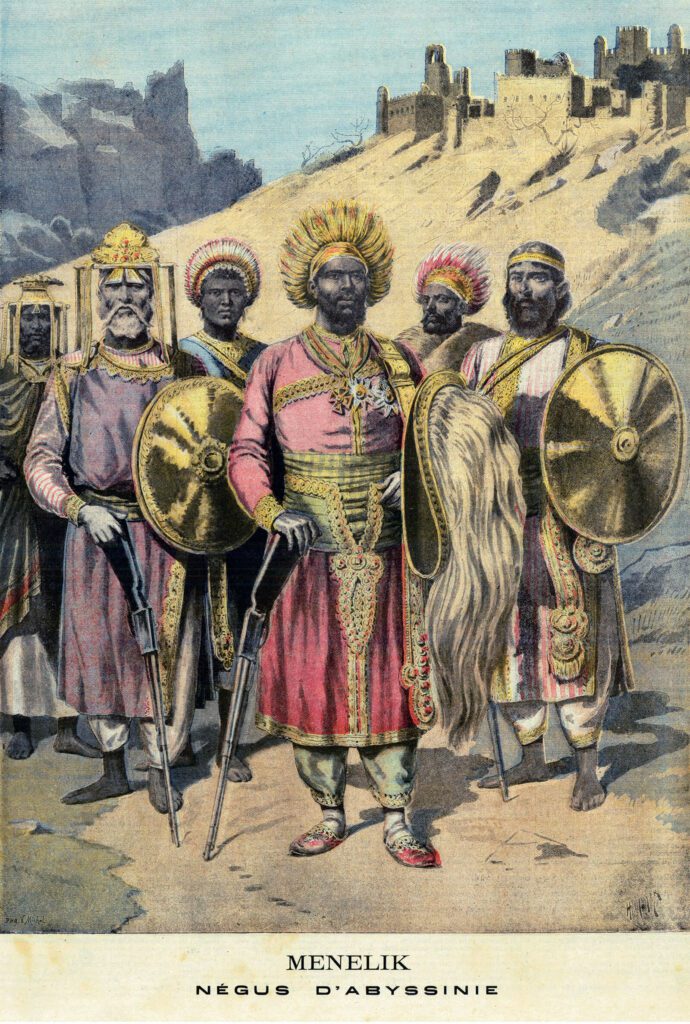
7. The Ethiopian Empire
It spread throughout several regions of what are now Eritrea and Ethiopia between 1137 and 1975 CE. On the map of African kingdoms, the empire lasted from the Middle Ages until the Cold War. It demonstrated its strength by fending off numerous adversaries who tried to encroach on its lands. The Ottoman, Italian, and Egyptian armies were a few of these. Some of its rulers are thought to be descendants of King Solomon. After the Italians won the Second Italo-Ethiopian War in 1935, the monarchy was overthrown.
8. The Kingdom of Kongo
A portion of the DRC, Angola, Republic of Congo, and Gabon are now part of this empire. It existed between roughly 1390 and 1914 CE, when the European nations started vying for control of Africa. Luken Lua Nimi, a Kikongo warrior, was in charge of it. As he ruled central Africa, his political and military prowess was widely regarded. Ivory, copper, pottery, and textiles were all traded in the empire.
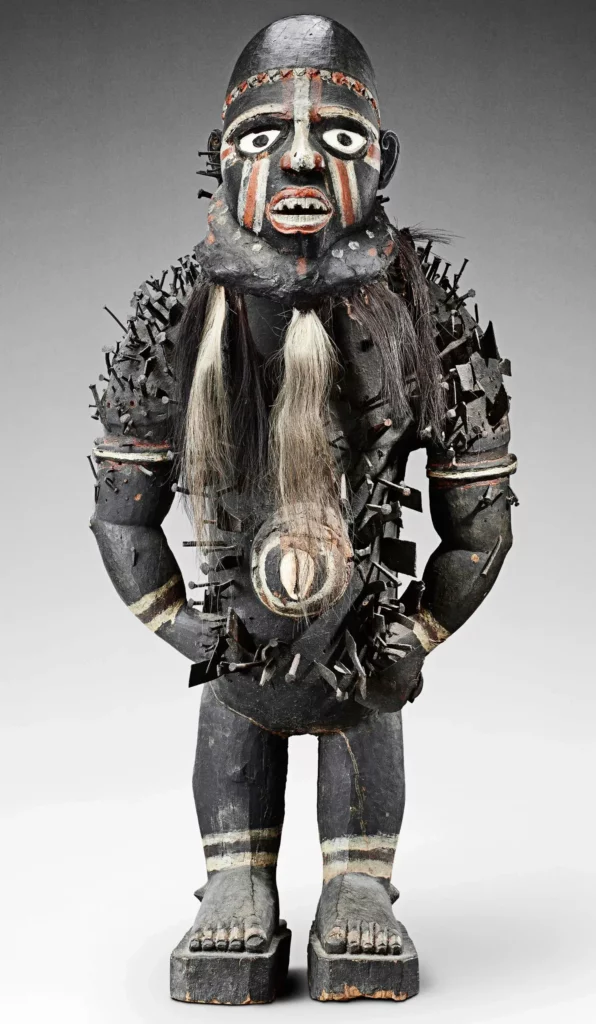
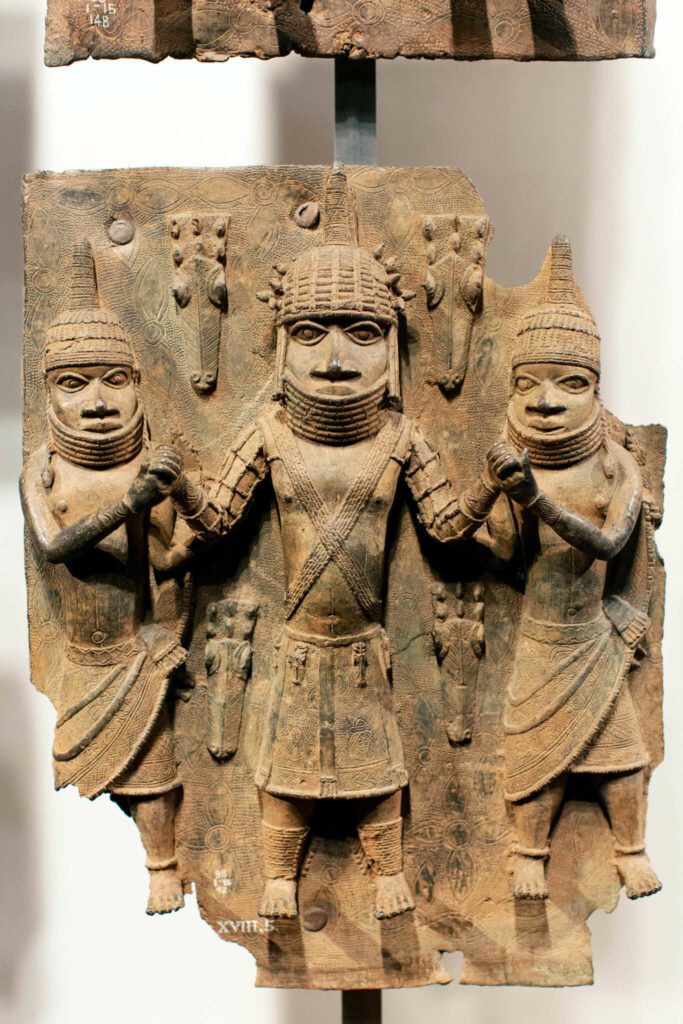


9. The Benin Empire
Between 1180 until 1897, this kingdom spanned present-day Nigeria. Among the different West African kingdoms, it was regarded as one of the oldest and most advanced. It exchanged manila and firearms for bronze, ivory, iron, pepper, and palm oil. Additionally, it was one of the African kingdoms that the British Empire subdued.
10. The Kingdom of Kush
For more than a thousand years, this empire dominated the continent of Africa as a strong regional force. It crossed what is now Sudan, however it is frequently eclipsed by Egypt’s neighbors to the north. The empire possessed control over a significant area of land around the Nile River.
It is thought that Egyptian sources account for the most of what is known about it. They traded in incense, gold, iron, and ivory. It’s interesting to note that they both constructed their pyramids and revered various Egyptian deities. The dead were also mummified by them.

Travel to Ethiopia
Ethiopia is a rugged, landlocked country in the Horn of Africa divided by the Great Rift Valley. It's a place of ancient culture, with archaeological finds dating back more than 3 million years.
History of Ethiopia
Ethiopia is bounded to the north by Eritrea, to the northeast by Djibouti, to the east by Somalia, to the south by Kenya, and to the west by South Sudan and Sudan.
People Of Ethiopia
Ethiopians are ethnically diverse, with the most significant differences based on linguistic classification. Ethiopia is a linguistic mosaic of about 100 languages divided into four groups.
A super quick guide to Addis Ababa
Addis Abeba, Ethiopia's capital, embraces contradiction like a spice, with sharp flavors that are rich in complexity. Luxurious metropolitan high rises coexist with humble makeshift dwellings.
8 of the best parks to explore in Addis Ababa
With all of its buzz and urban energy, Addis Ababa has been undergoing a transformation, with an increasing number of parks sprouting up all over the city. Here are some of the best options for green space in town.
5 places to feel like you’re on safari without leaving Nairobi
Kenya is world-renowned for its incredible variety of fauna and flora, as depicted in the film Out of Africa and numerous wildlife documentaries.
Terminal 2: Etiopian Airlines Star Alliance Gold Lounge
- Opening hours: first to last departure of the day
- Services: premium food and snacks, WiFi, television, newspapers and magazines